Raysync -
The Fastest Enterprise File Transfer Solution
Raysync is a high-speed enterprise file transfer solution designed for rapid, bulk data transfers.
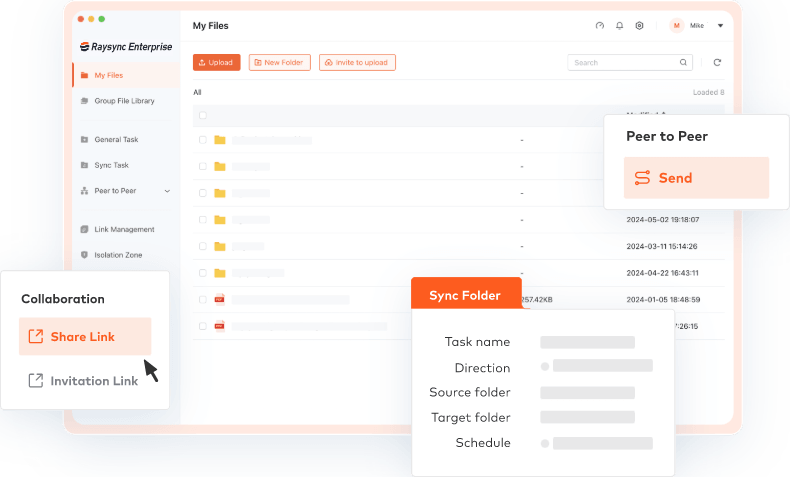





What Makes Raysync Special
Raysync, a leading enterprise file transfer solution, offers these key features.
High-Speed File Transfer
Transfer large files of any size, quantity, or format at the maximum speed within your bandwidth without additional charge for transfer volume.
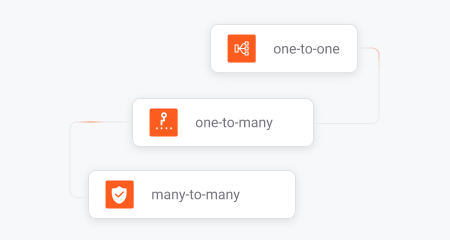
Auto File Sync & Backup
Provides versatile synchronization options, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many, as well as incremental backup and more.
Massive File Transfer
Transfers thousands of small files per second for maximum efficiency.
Peer-To-Peer Transfer
Send and receive large files directly between devices via peer-to-peer transfer.
Easy-to-Use Interface
Intuitive interface for quick onboarding.
SDK & API Integration
Seamless integrate Raysync with current system or application.
Your Complete Enterprise File Transfer Solution
Let's really dig into how you manage file transfers with Raysync
Various Options for Rapid File Transfer
- Blazing fast uploads and downloads
- Securely share exchange content with global partners.
- Auto-sync your files to ensure your data is always backed up.
- Direct peer-to-peer file transfers.
Take Control of File Transfers at Work
- Onboard new team members with easy user setup.
- Manage user permissions with granular control.
- Track and monitor all file transfer activity.
- Fully customizable interface with corporate identity.
- Hybrid cloud/on-premise configurations to fit your workflow.
Flexible Pricing Options for Every Business
Raysync offers scalable, high-speed large file transfer solutions for everyone, from teams to major corporations.
Raysync Enterprise
For large enterprises with complex needs, Raysync Enterprise offers a comprehensive, secure, and scalable file transfer solution.
Raysync SMB
Raysync SMB provides a cost-effective enterprise file sharing solution for small and medium businesses needing fast, unlimited file transfers, ideal for teams of up to 10 people.
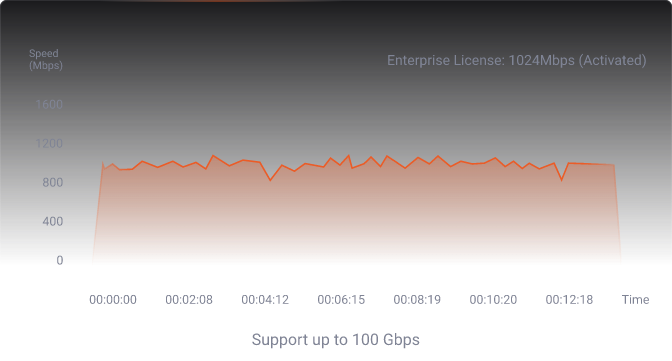
Raysync Speed Test: Enterprise Edition
See the real-world test about how long it takes to transfer 86GB file from France to Singapore with Raysync.
Advanced Encryption: Protecting Your Data
Raysync is also a secure file transfer solution that ensures business data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
See Why Businesses Love Raysync
Discover why businesses worldwide have chosen Raysync as their trusted file transfer solution.
“To the Raysync team, I would like to express our sincere appreciation for your dedication, responsiveness, and commitment to innovation. Your team's deep understanding of our industry's unique challenges has been invaluable.”
Boopathy Thangamuthu
IT Manager at Phantom FX

“Traditional FTP solutions are inadequate for our needs, as we require the transfer of large amounts of data within very short timeframes while utilizing available bandwidth efficiently. Raysync has proven to be an excellent solution for our requirements.”
Bhavik Sukhadia
Head of Technical Operations and Production Engineering at Fractal Picture

“As Gulfsat's Broadcast Core Expert, I've found Raysync's solutions exceptional for our operations. Their high-speed file transfer technology delivers remarkable efficiency and security while seamlessly integrating with our broadcast infrastructure.”
Danish Faraz
Broadcast Core Expert at Gulfsat Communications
100x
Faster
than using FTP to transfer files.
99%
Bandwidth Utilization
achieved by Raysync High-speed transfer Protocol.
10,000+
Business Clients
achieved by Raysync High-speed transfer Protocol.
Discover More About Raysync
Raysync as an Alternative to
Raysync File Calculator
Fresh Content

7 Fast File Transfer Software Utilities Prioritizing Speed
In today's digital landscape, secure file sharing is paramount. This blog post introduces the top three secure file transfer solutions designed to protect your sensitive data from cyber threats.
Learn more
How To Send Large Files Fast? 5 Methods for You
We’ve all been there—staring at a progress bar that’s moving at a snail’s pace, wondering if your massive file will ever reach its destination. Whether it’s a video project, a high-resolution photo collection, or a crucial business document, fast large file transfer is often a challenge, especially when the dead line is coming. But it doesn’t have to be! In this blog post, we’re diving into the best methods to send large files fast, so you can stop waiting around and get back to what really matters. Let’s get started!
Top 7 Bulk Files Transfers [Free&Paid]
Sending bulk files can be a daunting task. In 2024, there are efficient tools available to simplify the process. This guide introduces the top 7 bulk file transfer tools, designed to handle large file transfers with speed, reliability, and ease.