Everything You Need To Know About Peer-to-Peer Transfer
November 21, 2022
Introduction
A peer-to-peer connection in telecommunications relates to a communication between two terminals or nodes. Peer-to-peer is shortened to P2P sometimes. In sharing platforms or in other data-sharing protocols between people, this use of P2P is separate from the use of P2P which means peer-to-peer. For instance, a telephone call when one phone is connected to another, and only the others could hear what one caller says. In contrast, this is a topology for point-to-multipoint or broadcast communication, where several nodes can receive information from a node. Additional instances of peer-to-peer links include leased lines, microwave relays, and two-way radio. For example, radio and television broadcasts are points-to-multiple.
- Have you used P2P? P2P transfer is now widely used to share files by many enterprises in their work after LAN, FTP, and HTTP are outdated.
- P2P transfer, known as peer-to-peer transfer, is an instant file transfer mode, which aimed to enable all clients to provide resources, including bandwidth, storage space, and computing capacity. P2P transfer technology has wide application scenarios, such as audio, video, and data sharing in various formats.
- How does P2P technology transfer files instantly? Why P2P transfer is accepted widely by many enterprises? In this article, let’s start with these two questions and explore the answers to peer-to-peer transfer.
Everything about P2P Transfer in One Picture
With the growing number of IP cores combined on one chip, the system-on-chip (SoC) architecture is able to deploy complicated applications. The enormous need for communication and the ample computing capability on the chip put a considerable burden on the architecture in communication. Scalable communication architectures are therefore needed to implement future systems efficiently. Two types of communication systems, namely peer-to-peer (P2P) and bus-based designs have traditionally been explored. At the expense of the specific channels between all communicating IP pairs, P2P communication designs can provide the most communication performance. However, in terms of high complexity, expense, and design effort these designs are poorly scalable. By contrast, bus systems can connect a few dozen IP cores economically and eliminate the complexity of the system and the specific cables required by P2P systems.
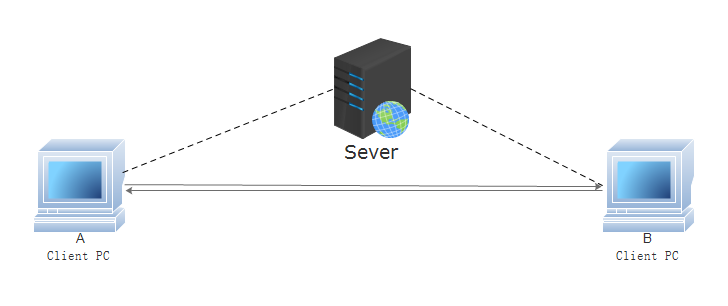
The traditional HTTP transfer is to copy data to the client via server, thus the transfer speed is restricted by the bandwidth. Especially in today's network environment, the large amount of clients connects to one server, the bandwidth of servers will be shared, and the bandwidth of clients is difficult to be fully utilized, resulting in low efficiency of overall data transfer. In general data transfer, client A and client B is essential to build a connection to the server, and then data will be transfer through the channel built by the server and data recipient. P2P transfer technology builds the direct channel between client A and client B, shorten the original upload-download "1+1" time to 1; Secondly, "client A-server-client b" is turned to "client A-client b", which does not transit through the server and does not consume the expensive storage space of the server.
Figure 1. P2P Transfer in One Picture
Cons & Pros of P2P Transfer
P2P technology is popular in many industries such as film and media, Internet TV, telemedicine, it not only provides freedom and facility to data transfer but also integrates all potential Internet resources. In technical expert’s opinion, P2P transfer is a kind of instant technology for quick data moving and sharing, it is beneficial to creating opportunities for enterprises in today’s market environment driven by data. However, with 5G emerging and the continuous development of information technology, P2P transfer is undoubtedly a double-blade sword, so it’s difficult for enterprises to step forward.
Pros:
- Low cost: save the cost on the server.
- Efficiency improved: remove the intermediate procedures and establish simple connections.
- High stability: eliminate the server-centered single-point service in the past, form the decentralized P2P transfer organization, which solved the fault problem caused by the central single point.
Cons:
Network bandwidth resources are consumed in large quantities: The concurrent connection of P2P transfer makes the resources consumed in large quantities, it is easy to cause network congestion and reduce the performance of other applications.
Inconvenient management: The P2P transfer is decentralized, the amount of users is huge thus it’s hard to take care of all users.
Security risks of data leakage: The widely use of P2P transfer leads to someone use the loopholes in the system to invade user privacy and destroy data. Some criminals even add viruses in the P2P transfer process, which poses a threat to users' computer security.
The P2P transfer technology is not strong enough to satisfy enterprises’ various needs, therefore, there must be a breakthrough. According to whether the clients are in the same network environment, the difficulty degree of P2P transfer technology is different. What modern technologies can be used to optimize and how to optimize? Let's continue to explore the principle of P2P technology and try to find a breakthrough.
P2P technology upgrading Based on NAT+Raysync
The transmission protocol of Raysync has abandoned the use of transmission messages as both byte counts and TCP protocol. With its revolutionary UDP transmission method, Raysync overcomes faults in existing TCP-based file transfer protocols (such as FTP and HTTP). The transmission speed of FTP/HTTP is hundreds of times higher and is not reduced by the size of the file, transmit distance, or network difficulties. Raysync can offer secure internal and external sharing of data, enabling you to securely upload, download and edit files on a user-friendly interface. Send huge files via mobile devices and web browsers in every location and anywhere.
Characteristics
Raysync transmission protocol may make full use of a broad network of bandwidths for the fastest transfer of data. It can enable users in the huge data distribution application scenario to finish the big data transfer in the least time.
The multi-channel parallel transmission feature of the link is supported by RaySync Transmission Protocol. When a client interfaces between point B and point A, a multiplicity of unrelated data streams can quickly be transferred in Parallel via the multi-parallel channel property. The transfer of these data streams does not require the handshake connection process, which considerably enhances the transmission in real-time.
Raysync transmission protocol is UDP-based and may transit over various NAT devices smoothly.
Here we divided into two situations for analysis:
On the same network
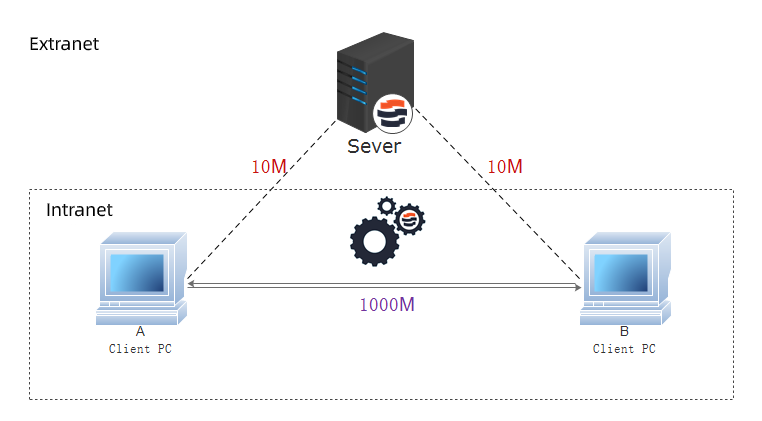
Assume that the internal network interface is 1000M, the LAN bandwidth is 10M, and the bandwidth utilization rate is 50%. Client A and Client B are in the same network environment, as shown in the following figure. If the traditional file transfer method is adopted, the A user needs to upload the file to the server first, and then B can download it from the server, there only 10M network bandwidth will be utilized in the whole transfer process. While through peer-to-point transfer, A and B can directly establish a connection, file transfer makes full use of the network bandwidth of 1000M, and the transfer efficiency can be improved by 100X.
Figure 2. P2P technology on the same network

Raysync combined the P2P technology with Raysync ultra-high-speed transfer protocol, the network bandwidth is fully utilized up to 96%. The file transfer process is accelerated, the TB-level big data and massive data transfer have never been easier.
Figure 3. P2P technology upgrading Based on NAT+Raysync
On the different network
Client A and client B are in two different network environments, and they need to try to connect with the target end to judge whether they can penetrate the network to establish communication. The P2P transfer between two clients will be different according to different clients. Several common P2P transfer methods through middleware include Relaying, Connection reversal, UDP hole punching. Through the following characteristic comparison table, we can simply grasp the characteristics and application scenarios of these methods.
Table 1. Characteristics and compassion table

According to the methods listed above, Raysync P2P transfer will try to connect with the recipient end in priority. If it is failed to connect, it will be connected by reverse connection or UDP punching. If it is still failed to connect, then the server transfers (relaying) will be adopted. Raysync will automatically select the best transfer mode in the whole process, reduce the network burden and make full use of network resources. Besides, the P2P transfer based on UDP needs to consider the type of NAT, because the penetration ways of different NAT combinations are not consistent, some can penetrate, while some cannot.
Figure 4. P2P technology on the different networks

Digging deep into NAT penetration technology, Raysync combines more than 10 NAT penetration technologies with Raysyncb ultra-high-speed transfer protocol and simultaneously applies on P2P transfer. In practical application, the penetration effect of these 10 NAT combinations can meet the current P2P transfer needs. Even in the face of a few impenetrable situations, Raysync may still be able to improve the transfer efficiency and find the optimal solution for P2P transfer.

A More Universal P2P Transfer through Innovation on Speed and Management
Transfer acceleration ensures efficiency improving
In the peer-to-peer transfer, the patented Raysync ultra-high-speed transfer protocol is adopted. This protocol can eliminate the bottleneck at the bottom layer, it is immune to limitation of the traditional network and hardware, fully utilize the network bandwidth, and realize ultra-low latency, high speed, and end-to-end output service, the transfer rate is improved by nearly one hundred times, thus easily achieves the safe, controllable and stable transfer of TB-level large files and massive small files.
Figure 5. P2P technology on the different networks about penetration and acceleration

Comparison of the peer-to-peer transfer efficiency
Test environment:
- Shenzhen-Beijing, network latency 35ms~45ms, packet loss rate 1%
- Server: Alibaba cloud Shenzhen, CentOS 8.3, 2 vCPU 4 GiB, bandwidth 100M, SSD disk
- ClientA: Alibaba cloud Shenzhen, CentOS 8.3, 2 vCPU 4 GiB, bandwidth 100M, SSD disk
- ClientB: Alibaba cloud Beijing, CentOS 8.3, 2 vCPU 4 GiB, bandwidth 100M, SSD disk
File transfer is automatic
For team collaboration, Raysync supports automatically receive peer-to-peer files from your partners. Compared to the traditional P2P transfer method, Raysync saves your time spend on manually file reception. The auto file reception can be realized with one click to enable the “Allow to receive transfer files from partners” button.

A data asset is strictly monitored
The admin user can monitor every single task in the admin console. Enter Raysync admin console – peer-to-peer transfer, you could view the peer-to-peer transfer account, IP, task name, receiver ID, country, states, city, total file transmission quantity, and transmission speed. In the meantime, it supports viewing the details of the peer-to-peer transfer task being transmitted and stopping the operation, and supports one-click viewing and downloading for historical transfer tasks.

All files and individuals traceable, each P2P task can be controlled by the admin. The comprehensive upgrade made by Raysync on P2P transfer overcomes the drawbacks of file and user management, enables peer-to-peer transfer to better meet the enterprise needs, and helps enterprises manage data more efficiently.
Bank-level data security
Based on the needs of customers in industries such as film and media, IT Internet, Raysync adopts AES-256+TLS encryption technology between client and server to guarantee end-to-end data security.

Aiming at the port problem, Raysync only needs to expose one port, which can meet all users' access needs and greatly reduce the risk of firewall port exposure; Hash verification protection is carried out at the transfer message level, file block, and the whole file to ensure the integrity of the transfer content. The optimization made by Raysync on peer-to-peer transfer, which has outstanding performance in performance, reliability, and security. The upgraded management design meets the needs of modern enterprises. As a one-stop solution provider for large file transfer, Raysync can be used as a tool for enterprises to realize fast file cooperation, and can also be used as an enterprise data management platform to provide data transfer services for industries such as film and media, finance, IT Internet, etc.
You might also like

Raysync News
June 7, 2023Raysync's large file transfer system supports multi-storage file transfer, which can meet the needs of businesses as storage types become more varied and complex.

Raysync News
November 21, 2022P2P transfer, known as peer-to-peer transfer, is an instant file transfer mode, which aimed to enable all clients to provide resources, including bandwidth, storage space, and computing capacity.

Raysync News
December 22, 2023As the volume of healthcare data grows, the transmission of healthcare data has become a major challenge for the healthcare industry. This article focuses on the knowledge of medical data transmission.