How Does Raysync Realized Multi-storage File Transfer
June 7, 2023
Currently, most large file transfer systems only support single storage, which cannot meet the diverse needs of businesses as storage types become more varied and complex, and business requirements become more complicated. To achieve high flexibility in placing different types of storage on the same server, Raysync adopts virtual path method to uniformly manage different object storage, paths, and network disks, allowing for the addition and deletion of storage and the upload or download of files from storage at any time. Let's take a closer look at how this is achieved.
In the server backend, you can add the storage information you want to access, including the storage ID, actual path, account name, and password. With this storage information, the server can connect to the storage and perform operations on its files. Raysync supports local storage, Alibaba Cloud, Amazon, Google Cloud, Azure Blob, and other S3-compatible object storage.
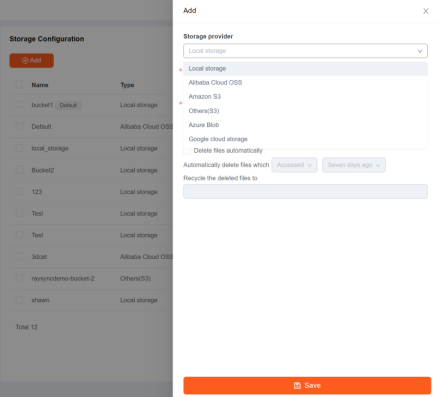
Set the logical root path of the server to "/".
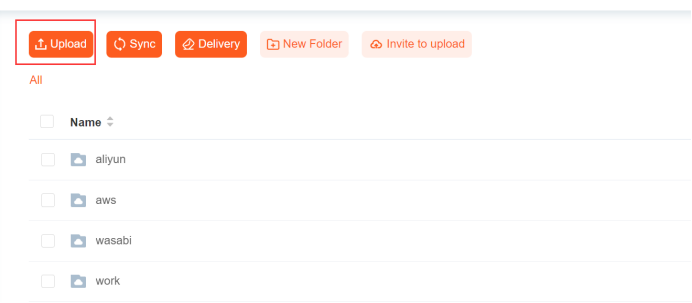
In the server backend, add a virtual directory for the users, starting with the server's logical root path "/" and then adding the desired path, for example, "/aws". At the same time, bind a storage ID to this virtual path.
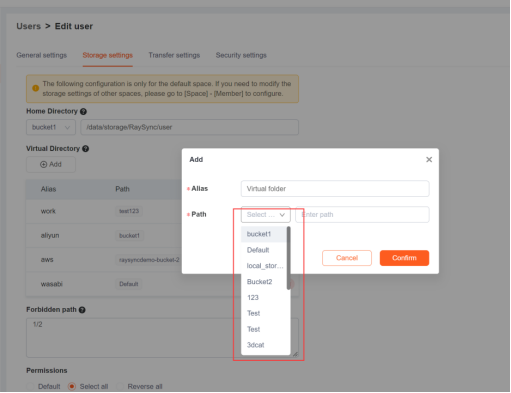
To uniformly manage various object storages, paths, and cloud drives, it is necessary to create multiple virtual directories.
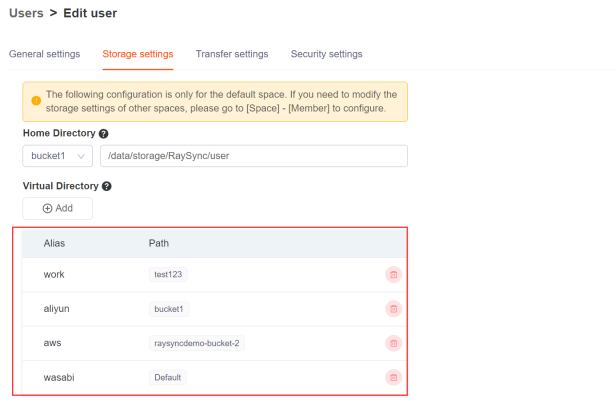
When a user client accesses a virtual directory, the server returns all the virtual paths under the logical root path. For example, it returns "/aws".
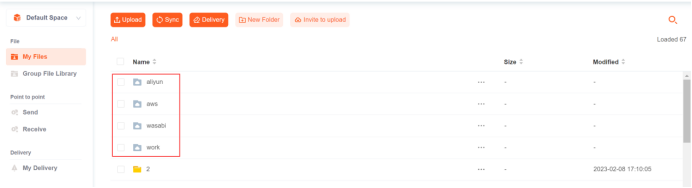
When the user client continues browsing "/aws", the server receives the request and looks up "/aws" in the virtual path list to get the bound storage ID. Then, it retrieves the storage information by using the storage ID and connects to the storage to traverse the actual path of the storage and obtain the file information under the actual path, such as "/aws/a". At the same time, it looks up all virtual paths under "/aws" in the virtual path list, such as "/aws/virtual path". Finally, it returns the obtained file information and virtual paths to the client.
After receiving the browsing results, the user client can begin to manage, add, and delete files, as well as upload and download files between different storage locations.
You might also like
Raysync News
January 24, 2024The connectionless and unreliability of UDP also brings a series of challenges, especially when the data transfer speed is too fast. This article will explore these problems and introduce the solution.

Raysync News
January 5, 2024Facing major challenges in the healthcare sector, RaySync is empowering the modern and rapid development of data transfer in the healthcare industry.

Raysync News
November 19, 2020This article mainly introduces several forms of high-speed data transmission, including UDP, UDP, TCP and other transmission methods.