Detailed Explanation of P2P File Sharing [Latest Update]
July 10, 2024In today's digital age, sharing files quickly and efficiently has become essential. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing is one of the most popular methods used for this purpose. It allows users to exchange files directly without relying on a central server, making the process faster and more decentralized.
In this blog, we will dive deep into how P2P file sharing works, its benefits, potential risks, and the latest updates in the technology. Whether you're new to P2P or looking to stay informed about the latest developments, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of P2P file sharing.

What Is P2P File Sharing
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing is a decentralized method of distributing or sharing files across a network. In a P2P network, each participant, referred to as a "peer," acts both as a client and a server. This means that every peer can upload and download files simultaneously, directly communicating with other peers without needing a central server.
In traditional file-sharing systems, a central server holds all the files, and users download files from this server. In contrast, P2P file sharing breaks the files into smaller chunks and distributes them across multiple peers in the network. Each peer shares pieces of the file with others until every peer has the complete file.
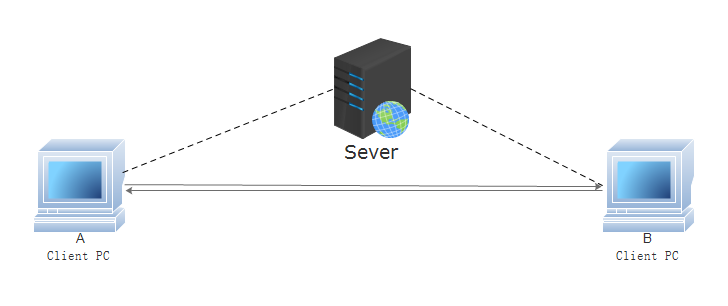
This method offers several advantages:
- Efficiency: By distributing the load across many peers, P2P file sharing can often result in faster download speeds, especially when many peers are sharing the same file.
- Resilience: Without a central server, the network is less vulnerable to failures or attacks. Even if some peers go offline, the file can still be downloaded from others.
- Scalability: As more peers join the network and share files, the overall capacity and speed of the network increase.
However, P2P file sharing also comes with potential risks, such as exposure to malicious files and copyright infringement issues. It's crucial to use P2P networks responsibly and be aware of the legal and security implications.
In the next sections, we will explore the mechanics of P2P file sharing, its various applications, and the latest updates in this ever-evolving technology.
Is P2P File Sharing Illegal
The legality of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file sharing depends on what is being shared and how it is being distributed. Here are some key points to consider:
- Legitimate Uses: P2P file sharing itself is not inherently illegal. It is a technology that can be used for many legitimate purposes, such as distributing open-source software, sharing public domain content, or collaborating on projects. For example, many Linux distributions are available for download via P2P networks.
- Copyrighted Material: The legal issues arise when P2P networks are used to share copyrighted material without permission. Sharing or downloading movies, music, software, or other copyrighted content without the authorization of the rights holder is illegal in most countries and can result in legal consequences.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Different countries have different laws regarding intellectual property and file sharing. In some regions, copyright enforcement is stricter, and authorities may monitor P2P networks to detect and prosecute illegal file sharing.
- Terms of Service Violations: Even if the content being shared is not strictly illegal, using P2P networks can violate the terms of service of your internet service provider (ISP). Some ISPs may restrict or throttle P2P traffic due to the high bandwidth usage.
- Security Risks: Beyond legality, P2P file sharing can pose security risks. Downloading files from unknown sources can expose users to malware, viruses, and other malicious software.
How to Start Secure P2P File Sharing
Starting secure P2P file sharing involves a few key steps to ensure that your activities are both legal and safe. Here’s a guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Choose the Right P2P Software
Select a reputable P2P file-sharing application that is known for its security features. Some popular and reliable options include:
- BitTorrent: One of the most well-known P2P protocols, with many clients to choose from, like qBittorrent and uTorrent.
- eMule: A popular choice for sharing files over the eDonkey network.
- FrostWire: A P2P client that also supports torrenting, known for its built-in search capabilities.
Step 2: Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN encrypts your internet connection and hides your IP address, providing an extra layer of security and privacy. Here’s what to look for in a VPN:
- No-logs policy: Ensure the VPN does not keep logs of your activity.
- High-speed servers: For fast and efficient file sharing.
- P2P support: Not all VPNs support P2P traffic, so choose one that does.
Some popular VPNs for P2P file sharing include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and CyberGhost.
Step 3: Enable Security Features
Most P2P clients offer security features that you should enable, such as:
- IP Filtering: Blocks known malicious IP addresses.
- Encryption: Encrypts the data you share to prevent eavesdropping.
- Port Forwarding: Helps optimize your connection while maintaining security.
Step 4: Download from Trusted Sources
Only download files from trusted and reputable sources to avoid malware and other security threats. Look for verified torrents and read user comments and ratings before downloading.
Step 5: Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly update your P2P client and antivirus software to protect against new vulnerabilities and threats. Ensure that your operating system is also up-to-date.
Some Tools for Free Peer-to-Peer File Sharing
Here are some free yet excellent options to help you out if you are on a tight budget.
1. µTorrent
Starting with the top-notch option, µTorrent is renowned for its lightweight design and efficiency as a BitTorrent client. It stands out for its user-friendly interface that facilitates quick downloads and seamless management of bandwidth.

Users can prioritize downloads, set upload and download limits to optimize performance, and schedule downloads at specific times. uTorrent also supports RSS feeds for automatic downloading of new content, making it a versatile choice for users looking to efficiently manage their downloads without unnecessary complexities.
2. qBittorrent
qBittorrent presents itself as an open-source alternative to uTorrent, offering a similar interface while emphasizing transparency and user control. It boasts an integrated search engine to find torrents directly within the application, reducing the need for external sources. qBittorrent supports sequential downloading, enabling users to preview files while they are still downloading.

Moreover, it fully embraces magnet links, a feature increasingly popular for starting downloads without needing to download a separate torrent file. These qualities make qBittorrent a robust choice for users seeking a reliable, open-source P2P file-sharing solution.
3. BitTorrent
BitTorrent is not just a specific software application but also the foundational protocol behind P2P file sharing. Developed by Bram Cohen, BitTorrent revolutionized file distribution by decentralizing it across multiple peers. Unlike traditional methods where files are downloaded from a single server, BitTorrent allows files to be shared among peers, enhancing download speeds and efficiency.

It operates on a peer-to-peer architecture, where each user contributes to the distribution by downloading and uploading portions of the file simultaneously. Compatible with a wide range of operating systems, BitTorrent remains a cornerstone in the realm of P2P file sharing, known for its speed, reliability, and decentralized nature.
The Best P2P File Sharing Tool for Enterprises: Raysync
Raysync boasts a built-in peer-to-peer (P2P) file transfer feature that allows direct transfers between users without using their servers.
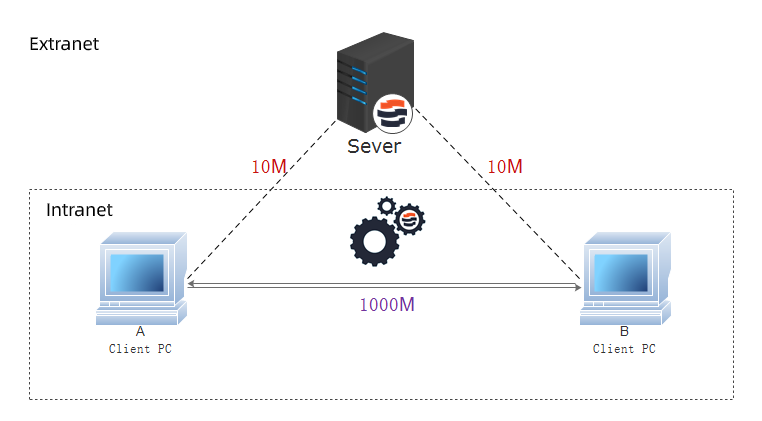
Here's what this means:
- Faster Speed: P2P leverages a direct connection between users, bypassing the Raysync servers. This can significantly accelerate file transfers, especially for large files.
- Reduced Reliance on Servers: Your transfer doesn't rely on Raysync's storage space or bandwidth, potentially leading to more consistent speeds.
Here's how to utilize Raysync's P2P functionality:
- Initiating Transfers: The sender provides a transfer ID and key, allowing the recipient to connect directly for the transfer.
- Security: While the transfer occurs directly, Raysync maintains a secure connection for traffic management.
Use Cases:
- Media and Entertainment: Sharing large video files, graphics, and other media assets among production teams.
- Healthcare: Transferring large medical images and records securely between healthcare providers.
- Engineering and Manufacturing: Collaborating on large CAD files and other technical documents across different locations.
- Financial Services: Ensuring secure and fast transfer of large financial datasets and reports.
FAQs about P2P File Sharing
Got a specific question related to P2P file sharing? Read on, below section might have the answer
Is it safe to share files on P2P?
Answer: P2P file sharing can be safe if you use reputable software, enable security features like encryption, and download from trusted sources. However, there are risks of downloading malware or copyrighted material illegally.
What is a risk of using P2P?
Answer: Risks include exposure to malware, legal consequences from downloading copyrighted material without permission, and potential security vulnerabilities if not using secure practices.
Is P2P banned in the US?
Answer: P2P technology itself is not banned in the US. However, certain uses of P2P networks to distribute copyrighted material without permission are illegal and can lead to legal action.
Wrap Up
In conclusion, P2P file sharing offers a decentralized and efficient way to distribute files across networks. By using trusted software, implementing security measures, and respecting copyright laws, users can enjoy the benefits of P2P sharing while minimizing risks. Whether you're sharing open-source software or downloading public domain content, understanding the legal and security implications is essential for a safe and responsible experience.
You might also like
![Top 5 FTP SaaS Solutions [Individual / Business]](http://images.ctfassets.net/iz0mtfla8bmk/4y0JMTNs8kAmi8I770y7Da/7bcc0be7cd0e11c4317099297f1aafb5/ftp-saas.png)
Industry news
December 12, 2024Explore the top 5 FTP SaaS solutions tailored for individuals and businesses. Learn about the features and pricing models of FTP SaaS, and how they simplify file transfers.

Industry news
September 12, 2024Find the best six file transfer automation software for seamless data transfers.

Industry news
July 25, 2024Discover the top 4 Resilio Sync alternatives. Explore detailed reviews of these alternatives along with their features, pros, cons, and free trial options.