Quick Answer: What Is the File Transfer Protocol
June 26, 2024Need to move files between computers? Ever heard of FTP? This post breaks down File Transfer Protocol (FTP) in a simple and easy-to-understand way. In a few minutes, you'll know exactly what FTP is and how it works!

Part 1: Definition of the File Transfer Protocol
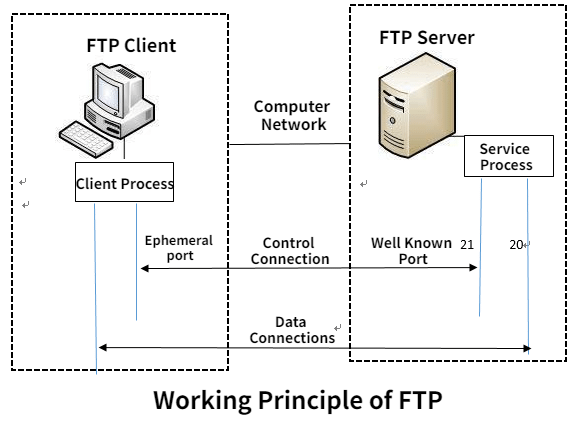
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a set of rules that governs how files are exchanged between computers on a network. It's like a common language computers use to upload and download files from each other.
Here's a breakdown of its key aspects:
- Function: FTP allows you to transfer files between a local computer (yours) and a remote server (another computer on the network).
- Simplicity: FTP is known for being relatively easy to use.
- Security: While convenient, a major drawback of FTP is its lack of robust security features. Sensitive information can be vulnerable during transfers.
Overall, FTP is a good starting point for basic file transfers, but for secure and feature-rich data exchange, consider exploring Managed File Transfer (MFT) solutions.
Part 2: Who Is Using the File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used by a wide range of individuals and organizations for various purposes. Here's a breakdown of some common users:
Individuals:
- Downloading files from public FTP servers (e.g., software updates, free resources).
- Uploading personal files to web servers (e.g., website content for hobbyists).
Businesses:
- Transferring large files internally between departments (e.g., design agencies sharing project files).
- Sharing data with vendors or partners securely (common in the pre-MFT era).
Educational Institutions:
- Distributing course materials to students (e.g., lecture notes, assignments).
- Uploading research data to public repositories.
Web developers and designers:
- Uploading website content to web servers is becoming less common due to security concerns.
- Transferring website development files between local machines and servers.
While FTP remains in use for some scenarios, it's important to note that more secure and feature-rich alternatives like Managed File Transfer (MFT) are becoming increasingly popular, especially for businesses dealing with sensitive data.
Part 3: Pros and Cons of the File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a workhorse of the digital world, but it has both advantages and limitations to consider. Here's a breakdown:
Pros:
- Simple and Easy to Use: FTP offers a user-friendly interface, making it easy to transfer files between computers, even for non-technical users.
- Widely Supported: FTP is universally compatible with most operating systems and devices, ensuring broad functionality.
- Free to Use: Many basic FTP servers are free to access, making it a cost-effective option for casual file transfers.
Cons:
- Security Concerns: A major drawback of FTP is its lack of strong security features. Usernames, passwords, and transferred data can be transmitted in plain text, making them vulnerable to interception.
- Limited Functionality: While efficient for basic transfers, FTP lacks features like automation, encryption at rest, and detailed audit logs, which are crucial for secure and regulated data movement.
- Outdated for Business Needs: As businesses handle more sensitive data and require stricter compliance, FTP's limitations become more apparent.
Part 4: Steps for File Transfer Protocol Download (Win and Mac)
This section provides a concise guide on how to download files using File Transfer Protocol (FTP) on both Windows and Mac operating systems. It includes instructions for using built-in tools and third-party FTP clients, ensuring users can efficiently transfer files regardless of their preferred method.
Method 1: Using a Third-Party FTP Client (FileZilla)
FileZilla is a popular FTP client available for both Windows and Mac. The steps are similar for both platforms.
- Download and install FileZilla.
- Launch the FileZilla application.
- Configure the FTP connection.
- Connect to the server.
- Browse the server.
- Download Files.
Method 2: Using Built-In Tools
For Windows (Command Prompt)
- Open Command Prompt: Press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
- Connect to the FTP server: type ftp.example.com and press Enter. Enter your username and password when prompted.
- Navigate to the Desired Directory: Use commands like cd (change directory) to navigate to the folder containing the files you want to download.
- Download Files: Use the get command to download a single file (e.g., get filename.ext).
- Use the mget command to download multiple files (e.g., mget * to download all files in the directory).
- Close the FTP session. Type bye to exit the FTP session.
For Mac (Finder)
- Open Finder: Click on the Finder icon in the Dock to open a new Finder window.
- Connect to Server: In the Finder menu bar, click on "Go" and select "Connect to Server" (or press Command + K).
- Enter the FTP address: Type the FTP address in the "Server Address" field (e.g., ftp://ftp.example.com) and click "Connect."
- Authenticate: Enter your FTP username and password if prompted.
- Browse and Download: The FTP server will appear as a mounted drive in Finder. Navigate through the directories to find the files you want to download. Drag and drop the files from the FTP server to your local machine to download them.
Part 5: Don't Miss: The Best File Transfer Protocol Alternative - Raysync
Raysync is a high-speed file transfer solution for enterprises, offering speeds up to 100 times faster than traditional FTP, keeping security in mind. It enhances productivity with efficient protocols and robust security features, which make it an ideal alternative for businesses needing efficient data transfer solutions.
Pros of Raysync:
- Raysync utilizes advanced technology and is 100 times faster than all traditional file transfer methods.
- It also implements AES-256 encryption and TLS, which means maximum protection and security.
- Raysync offers a modern alternative to FTP.
- Focuses on enhanced security and efficiency for file transfers.
- Features high-speed transfers with optimized protocols.
FAQs about the File Transfer Protocol
This section addresses common questions and concerns about File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
What is FTP and what are its uses?
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a standard network protocol used for transferring files between a client and a server on a computer network.
Uses: It facilitates uploading, downloading, and managing files on remote servers. Common applications include website maintenance, file sharing, and data backup.
Is FTP still used?
Yes, FTP is still widely used despite the security concerns associated with plain text transmission. It remains popular due to its simplicity, compatibility across different platforms, and ease of implementation.
What protocol would you use to transfer a file?
Secure protocols to transfer files, like SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) or FTPS (FTP Secure), are recommended.
SFTP uses SSH (Secure Shell) for encryption and authentication, ensuring data security.
FTPS implements TLS (Transport Layer Security) for encryption, providing secure file transfers over FTP.
Wrap Up
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) remains a fundamental tool for transferring files over networks globally due to its long history of use. However, FTP alternatives like Raysync offer enhanced security and efficiency, making them a more advisable choice in many cases. Understanding the pros, cons, and usage of FTP can help you make informed decisions for your file transfer needs.
You might also like

Industry news
March 14, 2025Upload speed very slow? Learn how to diagnose and fix slow upload speeds with these 6 expert steps.
Industry news
January 31, 2023aysync not only has powerful enterprise file synchronization function, but also has powerful file synchronization function and is easy to use, which makes people bid farewell to the tedious manual copying.

Industry news
February 14, 2025New to FTP Rsync? This beginner-friendly guide simplifies the process of setting up Rsync over FTP. Efficient file transfers are within reach – learn how here!
